问题
分析一个业务问题,具体背景如下:
100w单表数据集,业务主键和node_ids(list类型)字段,对业务主键创建了唯一索引,对node_ids字段创建了普通索引。
查询语句如下:db.client.find({"node_ids": {"$in": [","]}})。
该条件会匹配全量数据,简单说:会查全表。
在ssd的机器上,查询时间花费了10s。
WT原理
mongoDB 3.0以后默认的存储引擎是WiredTiger(WT)。 WT的核心特性:
- 文档级别的并行:WT使用乐观并发控制来检测冲突;MVVC
- 快照和Checkpoint
- 预写式日志
- 压缩
- 内存使用:WT使用独占的内存缓冲以及文件系统缓冲
WT存储引擎提供了基于Btree和基于LSM的数据存储能力。
WiredTiger maintains a table’s data in memory using a data structure called a B-Tree ( B+ Tree to be specific), referring to the nodes of a B-Tree as pages. Internal pages carry only keys. The leaf pages store both keys and values.
底层存储
- 面向行的存储:Btree,write-optimized
- 面向列的存储:将列族存储在不同的文件中,read-optimized
- Log-structured merge trees, bloom filter:write-optimized, 高吞吐量
内存优化的方向:
- 多核扩展
- 无锁/非阻塞算法
- 没有原地更新
- 最大化缓冲性能
磁盘优化的方向:
- 高效I/O:压缩、列存储、大型chunks
- LSM tree
B+tree和LSM性能对比
https://github.com/wiredtiger/wiredtiger/wiki/Btree-vs-LSM
性能Benchmark
https://github.com/wiredtiger/wiredtiger/wiki/LevelDB-Benchmark
性能优化
优化方向:
- 先预估性能开销
- 优化点:IN操作优化、索引优化、返回字段优化
性能预估
根据一个内存操作来预估在B+tree查找一个节点需要的时间:100ns(一次内存随机读写的时间); 进一步估算出读取100w需要多长时间。
IN操作优化
从下图可以看出:当IN 操作的参数数量不同时,对应的查询耗时也有所不同。
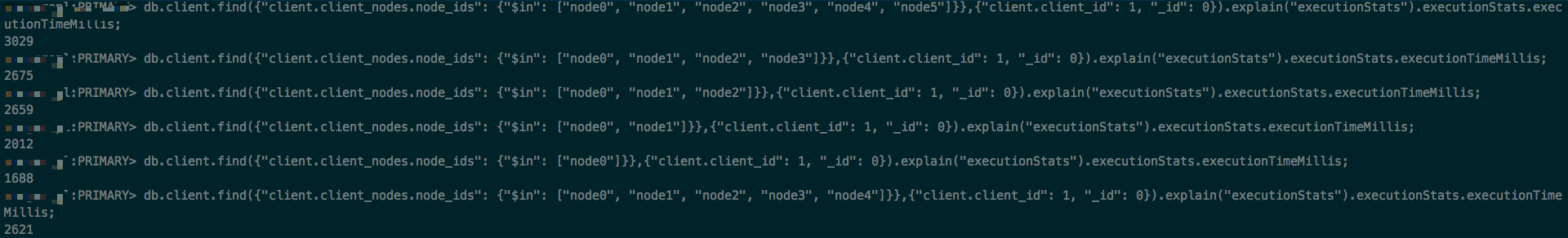
由于IN条件是关联查询的通用条件,对应的参数数量是由关联表的查询结果决定。
索引优化
索引类型:默认的unique _id索引、单字段索引、组合索引、multiKey索引(数组字段)、Geo索引、文本索引、哈希索引、唯一索引、离散索引、部分索引
在建索引时,如果索引字段值是数组,那么mongodb会为每个元素创建单独的索引条目。此时存在索引数据放大的情况。
覆盖索引:When the query criteria and the projection of a query include only the indexed fields, MongoDB returns results directly from the index without scanning any documents or bringing documents into memory. These covered queries can be very efficient.
对于mongodb, list类型无法使用覆盖索引。因此,只能使用普通索引
首先通过explain分析查询语句的性能开销:
mongorepl:PRIMARY> db.client.find({"client.client_nodes.node_ids": {"$in": ["node0", "node1", "node2", "node3", "node4", "node5"]}},{"client.client_id": 1, "_id": 0}).explain("executionStats");
{
"executionStats": {
"executionSuccess": true,
"nReturned": 637901,
"executionTimeMillis": 3792,
"totalKeysExamined": 1702364,
"totalDocsExamined": 637901,
"executionStages": {
"stage": "PROJECTION_DEFAULT",
"nReturned": 637901,
"executionTimeMillisEstimate": 368,
"works": 1702365,
"advanced": 637901,
"needTime": 1064463,
"needYield": 0,
"saveState": 13300,
"restoreState": 13300,
"isEOF": 1,
"transformBy": {
"client.client_id": 1,
"_id": 0
},
"inputStage": {
"stage": "FETCH",
"nReturned": 637901,
"executionTimeMillisEstimate": 303,
"works": 1702365,
"advanced": 637901,
"needTime": 1064463,
"needYield": 0,
"saveState": 13300,
"restoreState": 13300,
"isEOF": 1,
"docsExamined": 637901,
"alreadyHasObj": 0,
"inputStage": {
"stage": "IXSCAN",
"nReturned": 637901,
"executionTimeMillisEstimate": 241,
"works": 1702365,
"advanced": 637901,
"needTime": 1064463,
"needYield": 0,
"saveState": 13300,
"restoreState": 13300,
"isEOF": 1,
"keyPattern": {
"client.client_nodes.node_ids": 1
},
"indexName": "client.client_nodes.node_ids_1",
"isMultiKey": true,
"multiKeyPaths": {
"client.client_nodes.node_ids": [
"client.client_nodes.node_ids"
]
},
"isUnique": false,
"isSparse": false,
"isPartial": false,
"indexVersion": 2,
"direction": "forward",
"indexBounds": {
"client.client_nodes.node_ids": [
"[\"node0\", \"node0\"]",
"[\"node1\", \"node1\"]",
"[\"node2\", \"node2\"]",
"[\"node3\", \"node3\"]",
"[\"node4\", \"node4\"]",
"[\"node5\", \"node5\"]"
]
},
"keysExamined": 1702364,
"seeks": 1,
"dupsTested": 1702364,
"dupsDropped": 1064463
}
}
}
},
"operationTime": Timestamp(1645517306, 25)
}
通过IXSCAN可以看出,这条查询语句在查询时命中了索引。
executionTimeMillis 字段可知,整个查询语句花费的时间为3792毫秒。
executionTimeMillisEstimate 字段可知,实际在WT引擎上花费的时间大概在1秒左右
另外,存在2秒左右的时间开销用在别处:
- 由于list类型字段无法使用覆盖索引,涉及document
- server向client发送返回数据存在一定的时间开销
再次分析代码发现,Mongodb driver(golang)通过cursor获取数据(真正地与数据库进行通信)时。cursor.All函数使用了反射。
golang 在代码中使用反射是有一定性能开销的。 另外,mongodb数据库中schema模型是嵌套模型。这样会带来一定的数据序列化开销。
扩展
key value storage engine学习 https://stratos.seas.harvard.edu/files/stratos/files/keyvaluestorageengines.pdf
golang mongodb driver 通过batch方式和server进行通信的逻辑:
https://github.com/mongodb/mongo-go-driver/blob/master/x/mongo/driver/operation.go#L113
看起来很有意思的通用逻辑。